Contents
I. Introduction

Flush toilets have become an integral part of our modern lives, providing convenience and hygiene. However, their impact on the environment is often overlooked. In this article, we will explore the various ways in which flush toilets affect the environment and discuss potential solutions to mitigate their negative effects.
When we flush a toilet, the wastewater is transported through a complex system of pipes and treatment plants before being discharged into rivers, lakes, or oceans. This process consumes a significant amount of energy and resources, contributing to greenhouse gas emissions and water pollution.
One of the major environmental concerns associated with flush toilets is the excessive water usage. Traditional toilets can use up to 6 gallons of water per flush, which is a tremendous waste considering the global water scarcity. This not only depletes our freshwater sources but also puts a strain on the energy required to treat and transport the water.
Moreover, the chemicals present in cleaning agents and personal care products that are flushed down the toilet can contaminate water bodies and harm aquatic life. These chemicals, such as phosphates and surfactants, can disrupt the natural balance of ecosystems and pose a threat to both human and animal health.
Another issue is the improper disposal of solid waste. Flushing non-biodegradable items like wet wipes, sanitary products, and medications can lead to clogged pipes and sewage backups. These blockages not only require costly repairs but also contribute to the pollution of water bodies.
As the world becomes more conscious of its environmental impact, it is crucial to explore alternative solutions to traditional flush toilets. Water-efficient toilets, such as dual-flush systems and low-flow models, can significantly reduce water consumption. Additionally, composting toilets offer a sustainable way to manage human waste without relying on water-intensive systems.
II. Understanding Flush Toilets

Flush toilets are a common fixture in households around the world, but have you ever stopped to think about how they actually work? In this section, we will delve into the inner workings of flush toilets and explore their impact on the environment.
1. The Mechanism Behind Flush Toilets
Flush toilets operate on a simple yet effective mechanism. When you press the flush lever or button, water stored in the tank is released into the bowl. This sudden rush of water creates a force that pushes waste and wastewater down the drain and into the sewage system.
Inside the tank, there is a fill valve that allows water to enter the tank after each flush. This valve is connected to a float, which rises as the tank fills up. Once the water reaches a certain level, the float triggers the fill valve to close, stopping the flow of water into the tank.
Additionally, there is a flush valve at the bottom of the tank that opens when you flush, allowing water to flow into the bowl. This valve is connected to a flapper, which seals the opening when the tank is full and prevents water from continuously flowing into the bowl.
2. Water Efficiency and Conservation
One of the key concerns surrounding flush toilets is their water consumption. Traditional flush toilets can use a significant amount of water with each flush, contributing to water scarcity and higher utility bills.
However, advancements in technology have led to the development of low-flow toilets. These toilets are designed to use less water per flush, typically around 1.6 gallons (6 liters) or less. By reducing water consumption, low-flow toilets help conserve water resources and lower water bills for households.
Moreover, dual-flush toilets have gained popularity in recent years. These toilets offer two flushing options: a full flush for solid waste and a reduced flush for liquid waste. By providing different flush volumes for different types of waste, dual-flush toilets further enhance water efficiency.
3. Environmental Impact
While flush toilets provide convenience and sanitation, they also have a notable impact on the environment. The primary concern is the amount of water consumed with each flush, especially in areas experiencing water scarcity.
Additionally, the wastewater generated by flush toilets contains various contaminants and pollutants. When not properly treated, this wastewater can pollute water bodies and harm aquatic ecosystems. Therefore, it is crucial to have effective sewage treatment systems in place to minimize the environmental impact of flush toilets.
Furthermore, the production and disposal of flush toilets contribute to carbon emissions and waste generation. The manufacturing process involves the use of energy and resources, while the disposal of old toilets adds to landfill waste. Sustainable practices, such as recycling and using eco-friendly materials, can help mitigate these environmental concerns.
4. Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Like any other household appliance, flush toilets require regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance. Here are some common maintenance tasks and troubleshooting tips:
- Regularly check for leaks and fix them promptly to prevent water wastage.
- Keep the toilet bowl clean by using non-toxic cleaners and avoiding harsh chemicals.
- If the toilet is not flushing properly, check the flush valve and flapper for any obstructions or wear and tear.
- Consider installing a water-saving device, such as a toilet tank bank or a dual-flush conversion kit, to further reduce water consumption.
By following these maintenance practices, you can prolong the lifespan of your flush toilet and minimize its environmental impact.
III. Environmental Impact of Flush Toilets

Flush toilets have become a ubiquitous part of our daily lives, providing convenience and sanitation. However, it is important to consider the environmental impact of these modern plumbing fixtures. In this section, we will explore the various ways in which flush toilets affect the environment, including water consumption, energy usage, and pollution of water bodies.
A. Water Consumption
One of the primary concerns regarding flush toilets is their significant water consumption. Every time we flush, a substantial amount of water is used to carry away waste. According to studies, an average flush can consume anywhere between 1.6 and 7 gallons (6 to 26 liters) of water, depending on the toilet’s design and age.
Considering that the average person flushes multiple times a day, this water usage can quickly add up. In regions where water scarcity is a concern, such as arid climates or areas experiencing drought, the excessive water consumption of flush toilets becomes even more problematic.
To address this issue, water-saving technologies have been developed, such as dual-flush toilets. These toilets offer two flushing options: a full flush for solid waste and a reduced flush for liquid waste. By providing users with the choice to use less water when appropriate, these toilets help conserve water resources without compromising hygiene.
B. Energy Usage
While water consumption is a significant concern, flush toilets also contribute to energy usage. The energy required to treat and transport water to our homes, as well as the energy used in wastewater treatment facilities, should not be overlooked.
Water treatment plants consume a substantial amount of energy to purify and distribute water. Additionally, the transportation of water from its source to our homes involves energy-intensive processes, such as pumping and filtration. The more water we use through flush toilets, the greater the energy demand for these processes.
Furthermore, wastewater treatment facilities require energy to treat and process the flushed waste. These facilities use various methods, such as biological treatment and chemical disinfection, which rely on electricity. By reducing water consumption through efficient toilet designs and practices, we can indirectly decrease the energy demand associated with water treatment and wastewater management.
C. Pollution of Water Bodies
Flush toilets can also contribute to the pollution of water bodies. When we flush, the wastewater containing human waste, chemicals from cleaning products, and pharmaceuticals is transported through sewage systems to treatment plants or directly into water bodies.
Although wastewater treatment plants aim to remove contaminants before releasing the water back into the environment, they may not be able to eliminate all pollutants completely. Some substances, such as pharmaceuticals and microplastics, can be challenging to remove using conventional treatment methods.
As a result, these pollutants can find their way into rivers, lakes, and oceans, posing a threat to aquatic ecosystems and potentially entering the food chain. The accumulation of these pollutants over time can have long-term consequences for both the environment and human health.
To mitigate the pollution caused by flush toilets, it is crucial to raise awareness about proper waste disposal and the use of eco-friendly cleaning products. Additionally, investing in advanced wastewater treatment technologies can help improve the removal of contaminants and reduce the impact on water bodies.
IV. Alternatives to Flush Toilets
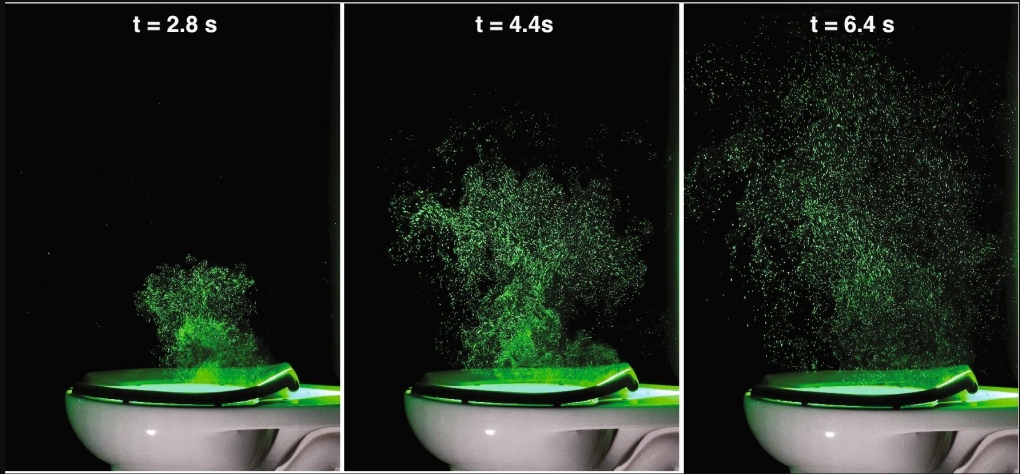
When it comes to sustainable living and reducing our impact on the environment, one area that often gets overlooked is our choice of toilets. Traditional flush toilets consume a significant amount of water and contribute to water pollution. Fortunately, there are several alternatives to flush toilets that are not only eco-friendly but also practical and efficient. In this section, we will explore three popular alternatives: composting toilets, vacuum toilets, and waterless toilets.
A. Composting Toilets
Composting toilets are a great option for those looking to minimize their water usage and reduce waste. These toilets work by breaking down human waste into compost, which can then be used as fertilizer for plants. The process is simple yet effective.
Composting toilets are designed to separate solid waste from liquid waste. The solid waste is mixed with organic materials such as sawdust or coconut coir, which helps facilitate the composting process. Over time, bacteria and other microorganisms break down the waste, turning it into nutrient-rich compost.
One of the key benefits of composting toilets is that they require little to no water. This not only helps conserve water but also reduces the strain on sewage systems. Additionally, composting toilets are odorless when properly maintained, making them a viable option for both residential and commercial use.
It’s important to note that composting toilets require regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance. The composting chamber needs to be emptied periodically, and the compost should be allowed to fully decompose before being used as fertilizer. However, with proper care and maintenance, composting toilets can be a sustainable and efficient alternative to traditional flush toilets.
B. Vacuum Toilets
Vacuum toilets are another innovative alternative to flush toilets that offer significant water savings. These toilets use a vacuum system to remove waste from the bowl, eliminating the need for large amounts of water to flush it away.
When a user activates a vacuum toilet, a powerful vacuum pump creates suction, pulling the waste into a sealed container. The waste is then transported through a network of pipes to a central collection point or a waste treatment facility. This process requires only a small amount of water to clean the bowl, resulting in water savings of up to 90% compared to traditional flush toilets.
Vacuum toilets are commonly used in commercial buildings, airplanes, and trains, where water conservation is crucial. They are also gaining popularity in residential settings, especially in areas with limited water resources or off-grid homes.
One of the advantages of vacuum toilets is their versatility. They can be installed in both new constructions and existing buildings, making them a practical option for retrofitting projects. Additionally, vacuum toilets are hygienic and odorless, thanks to the sealed system that prevents any unpleasant smells from escaping.
C. Waterless Toilets
Waterless toilets, as the name suggests, do not require any water for flushing. Instead, they use innovative technologies to separate solid waste from liquid waste and eliminate odors.
One type of waterless toilet is the incinerating toilet. These toilets use electricity or gas to burn the waste, reducing it to a small amount of ash. The incineration process is quick and efficient, and the resulting ash can be safely disposed of or used as a soil amendment.
Another type of waterless toilet is the dry composting toilet. Similar to composting toilets, dry composting toilets break down waste using natural processes. However, they do not require the addition of organic materials like sawdust. Instead, they rely on proper ventilation and the right balance of moisture and airflow to facilitate decomposition.
Waterless toilets are an excellent option for remote locations, off-grid homes, and areas with limited water supply. They are also popular in recreational vehicles (RVs) and boats, where water conservation is essential.
While waterless toilets offer significant water savings, they do require regular maintenance and may have higher upfront costs compared to traditional flush toilets. However, the long-term benefits in terms of water conservation and environmental impact make them a worthwhile investment.
V. Benefits of Using Environmentally-Friendly Toilets

As an environmentally-conscious individual and a passionate advocate for sustainable living, I have personally experienced the numerous benefits of using environmentally-friendly toilets. These innovative fixtures not only contribute to a healthier planet but also offer several advantages for homeowners and communities alike.
1. Water Conservation
One of the most significant benefits of environmentally-friendly toilets is their ability to conserve water. Traditional flush toilets consume a substantial amount of water with each flush, contributing to water scarcity and higher utility bills. In contrast, environmentally-friendly toilets utilize advanced flushing mechanisms, such as dual-flush systems or low-flow technology, to significantly reduce water usage.
By opting for these eco-friendly alternatives, households can save thousands of gallons of water each year. This not only helps to preserve precious water resources but also reduces the strain on municipal water treatment facilities. Additionally, lower water consumption translates to lower water bills, providing homeowners with long-term cost savings.
2. Energy Efficiency
Another advantage of environmentally-friendly toilets is their energy efficiency. Many modern toilets incorporate innovative features, such as pressure-assisted flushing or gravity-assisted flushing, that require less energy to operate. These mechanisms ensure effective waste removal while minimizing the need for excessive water pressure or electricity.
By reducing energy consumption, environmentally-friendly toilets contribute to a greener and more sustainable future. The energy savings achieved through these fixtures not only benefit individual households but also have a positive impact on overall energy demand and greenhouse gas emissions.
3. Waste Reduction
Environmentally-friendly toilets also play a crucial role in waste reduction. Traditional flush toilets often require large volumes of water to effectively remove waste, resulting in excessive water usage and strain on sewage systems. In contrast, eco-friendly toilets are designed to optimize waste removal while minimizing water requirements.
By utilizing advanced flushing mechanisms and efficient bowl designs, these toilets ensure effective waste removal with minimal water usage. This reduces the burden on sewage systems, lowers the risk of clogs and backups, and promotes more efficient wastewater treatment processes.
4. Improved Indoor Air Quality
Indoor air quality is a significant concern for many homeowners, especially those with respiratory conditions or allergies. Traditional flush toilets can contribute to poor indoor air quality due to the release of airborne particles and unpleasant odors during flushing.
Environmentally-friendly toilets, on the other hand, are designed to minimize these issues. Advanced flushing mechanisms and improved bowl designs help to reduce the release of airborne particles and odors, resulting in cleaner and fresher indoor air. This is particularly beneficial for individuals with sensitivities or respiratory conditions, creating a healthier living environment.
5. Enhanced Durability and Longevity
Environmentally-friendly toilets are often built with durability and longevity in mind. These fixtures are typically constructed using high-quality materials and advanced manufacturing techniques, ensuring they can withstand regular use and remain functional for extended periods.
By investing in an eco-friendly toilet, homeowners can enjoy the peace of mind that comes with a durable and long-lasting fixture. This eliminates the need for frequent replacements, reducing waste generation and saving money in the long run.
VI. Frequently Asked Questions
A. How do flush toilets impact the environment?
Flush toilets have a significant impact on the environment due to the large amounts of water they consume. On average, a single flush can use up to 6 liters (1.6 gallons) of water. This excessive water usage contributes to water scarcity, especially in areas with limited water resources. Additionally, the wastewater from flush toilets contains harmful chemicals and pathogens that can contaminate water bodies, leading to pollution and damage to aquatic ecosystems.
B. Are there any eco-friendly alternatives to flush toilets?
Yes, there are several eco-friendly alternatives to flush toilets that can help reduce water consumption and minimize environmental impact. One such alternative is composting toilets, which use little to no water and convert human waste into compost. Another option is the use of waterless urinals, which eliminate the need for flushing altogether. Additionally, low-flow toilets and dual-flush toilets are designed to use less water per flush, making them more environmentally friendly than traditional flush toilets.
C. How can I reduce water usage with a flush toilet?
There are several ways to reduce water usage with a flush toilet. One simple method is to install a water-saving device, such as a toilet tank bank or a displacement bag, which reduces the amount of water used per flush. Another option is to retrofit your toilet with a dual-flush mechanism, which allows you to choose between a full flush and a half flush, depending on the waste being disposed of. Additionally, fixing any leaks or running toilets promptly can help prevent unnecessary water wastage.
D. What are the benefits of using eco-friendly toilets?
Using eco-friendly toilets offers numerous benefits for both the environment and individuals. Firstly, eco-friendly toilets help conserve water, which is a precious resource. By reducing water consumption, eco-friendly toilets contribute to water conservation efforts and help address water scarcity issues. Secondly, these toilets minimize pollution and contamination of water bodies, ensuring cleaner and healthier ecosystems. Lastly, eco-friendly toilets can also lead to cost savings in terms of water bills, making them a financially viable choice in the long run.
E. Can flush toilets be made more sustainable?
Yes, flush toilets can be made more sustainable through various measures. One approach is the use of water-saving technologies, such as low-flow toilets and dual-flush mechanisms, which reduce water consumption without compromising functionality. Additionally, advancements in wastewater treatment technologies can help minimize the environmental impact of flush toilets. Implementing water reuse systems, such as greywater recycling, can also contribute to sustainability by utilizing wastewater for non-potable purposes like irrigation.

Michael Rasmussen is an accomplished writer with a passion for creating engaging content. Born and raised in a small town in Denmark, Michael developed a love for storytelling from a young age. He pursued his education at the prestigious Aarhus University, where he obtained a Bachelor’s degree in Literature and Creative Writing. With a unique perspective on life, Michael’s writing often delves into the intricacies of everyday experiences, including his quirky fascination with toilets. His ability to blend humor and insight has garnered him a loyal following of readers who appreciate his distinctive style. When he’s not busy crafting captivating narratives, Michael enjoys exploring the great outdoors and seeking inspiration in unexpected places.
